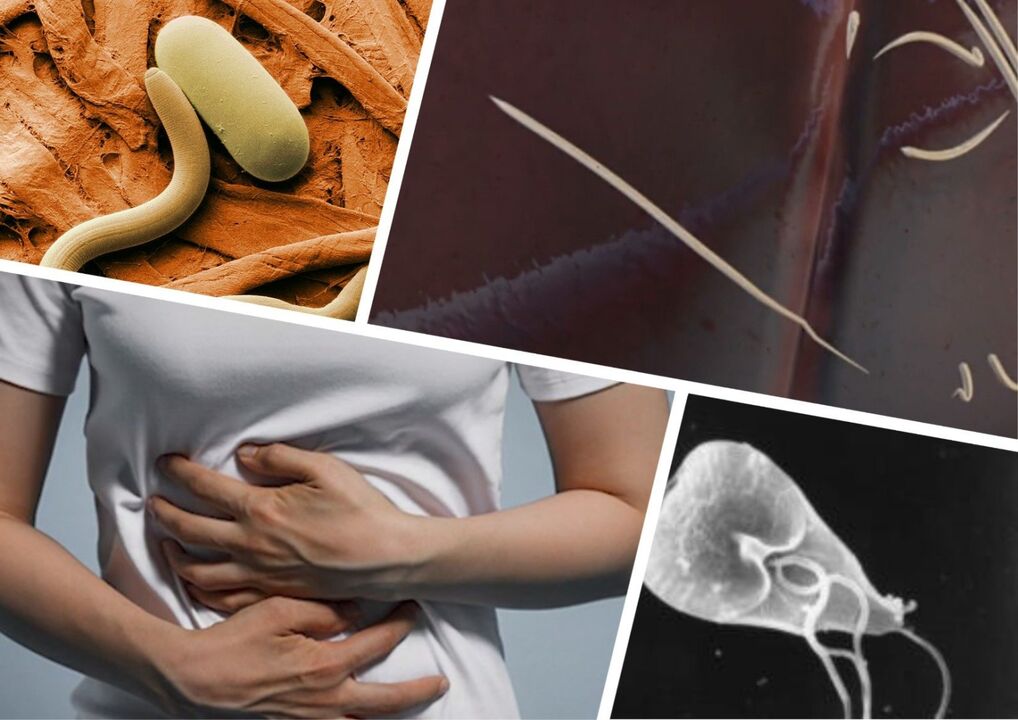
- In the chronic course of the disease, nutrients and protection are gradually depleted;
- More commonly, the body is invaded by hookworms, roundworms, Toxocara, and Trichocephala;
- Pathology is studied and treated not only in pediatrics and therapeutics, but also in gastroenterology, surgery, dermatology, allergology and other fields.
Causes and mechanisms
- Roundworms (nematodes): roundworms, pinworms (pinworms), whipworms (trichotillomatosis), nematodes (strongyloidiasis), hookworms, toxocara.
- Tapeworms (Tapeworms): Elongated tapeworm, Bovine and Pork tapeworm.
- Flukes (trematodes): Schistosoma.
Classification of helminthiasis
- Cysticercosis - hydatid, taeniasis, taeniasis;
- Nematodes - Trichocephalosis, Ascariasis, Nematodes;
- Trimatodes – Opiodiasis, Fascioliasis.
- worm;
- biological worms;
- Exposure to parasites.
- water;
- food;
- Transcutaneous.
- intestinal. They enter the host through the oral cavity and gradually spread along the gastrointestinal tract. The permanent habitat is the intestines. These parasites include strongyloidiasis, hookworm, and coccidiosis.
- parenteral form. Infiltration can also develop through the gastrointestinal tract, but then the parasite migrates through the intestinal wall to other organs. Such as blood vessels, subcutaneous fat, liver, brain. Opisthorchiasis, fascioliasis, and trichinellosis all share this property.
symptom
- nausea;
- decreased appetite;
- abdominal pain or cramping;
- abdominal bloating;
- flatulence;
- Diarrhea, constipation, their alternation.
- Headache;
- weakness, decreased performance;
- Changes in emotional background: depression, irritability, insomnia;
- thin;
- Pale skin, rash, visible pale and dry mucous membranes;
- dry cough;
- Frequent colds;
- Presence and frequency of bronchial asthma;
- Bruxism – grinding of teeth during sleep;
- Muscle and joint pain.
diagnosis
- Allergy skin test with added helminth antigen;
- Ultrasound examination of abdominal organs to evaluate the condition of the intestines, liver, spleen, and pancreas;
- Fiberoptic gastroduodenoscopy - a visual examination of the upper part of the digestive tract with a specific device introduced through the mouth;
- Colonoscopy - a visual examination of the wall of the large intestine by inserting a probe with a camera;
- Endoscopic biopsy – A section of tissue is removed during an endoscopy and is then subjected to microscopic examination and histological analysis;
- Radiographic or CT scans of internal organs with the addition of contrast media to assess the morphological properties of the tissue, detect foreign matter, and identify the integrity of the organ wall;
- Liver scintigraphy - Introduces a radioactive tracer that accumulates in the liver and emits radiation that is displayed on a monitor (can assess the organ's morphology, size, location, presence of defects).
treat
- anti-cystic drugs;
- Resistant to nematodes;
- Resistant to flukes;
- Has a wide range of effects targeting different groups of parasites.
- Antimicrobials, which cause additional complications of the condition by activating the pathogenic microbiota of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Adsorbents that encapsulate and remove worm poisoning products before they are absorbed into the systemic bloodstream;
- Enzymes that improve the digestive process, especially when helminthiasis is complicated by diarrhea;
- Probiotics – necessary when using anthelmintic and antibacterial drugs to restore normal intestinal flora;
- Cardiac glycosides treat complications of helminthiasis and cardiovascular disease;
- NSAIDs inhibit the active inflammatory process caused by the action of parasites;
- Glucocorticoids used to activate the immune system and develop acute allergic reactions.
prevention
- Wash hands and food frequently before eating;
- Maintain basic personal hygiene;
- administration of antiglycemic drugs to animals;
- heat treatment of meat and fish;
- Antihelmintics are used prophylactically, especially when characteristic symptoms occur or when the patient is at risk.
forecast
- Type of parasite;
- Worm distribution area;
- degree of poisoning;
- Complications of internal organs and systems.